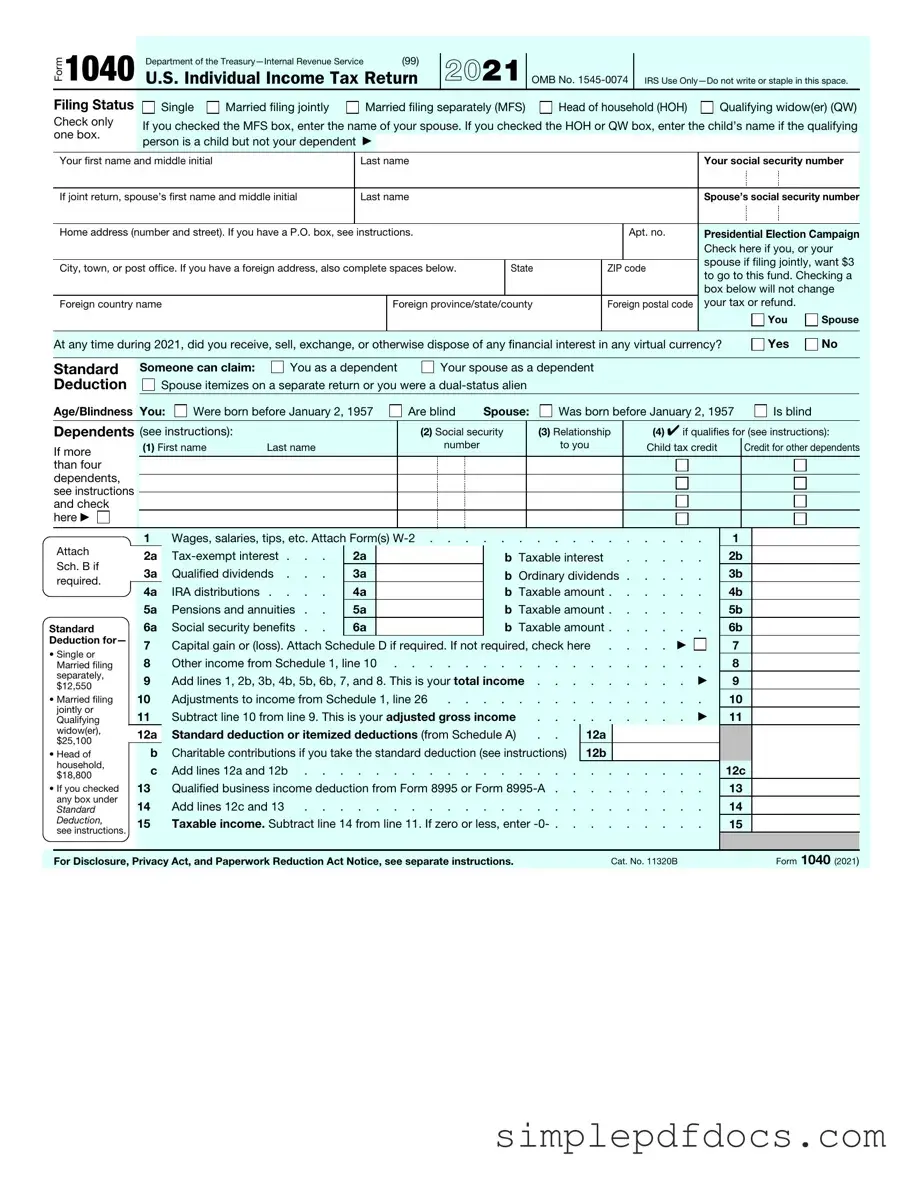
Fill Your IRS 1040 Form
The IRS 1040 form stands as a crucial document for individuals navigating the complexities of federal income tax filing in the United States. This form serves as the primary means through which taxpayers report their annual income, calculate their tax liability, and determine whether they owe additional taxes or are entitled to a refund. Each year, millions of Americans fill out this form, which requires the disclosure of various income sources, including wages, dividends, and capital gains. Additionally, the 1040 form allows for the inclusion of deductions and credits, which can significantly impact the overall tax owed. Taxpayers must also consider different filing statuses, such as single, married filing jointly, or head of household, as these choices influence the tax rates applied. Moreover, the form has undergone several revisions over the years, reflecting changes in tax law and policy, which can affect how individuals approach their tax obligations. Understanding the nuances of the IRS 1040 form is essential for ensuring compliance and maximizing potential refunds, making it a key component of the annual financial cycle for countless households across the nation.
More PDF Templates
Stock Transfer Form Companies House - Potential investors may review the ledger for insight into stock distribution.
U.S. Corporation Income Tax Return - Companies forming out of state may have special considerations for filing Form 1120.
When preparing for a vehicle transaction, understanding the importance of a reliable document is key. For a successful transfer, consider utilizing this thorough guide to the Tractor Bill of Sale, which outlines the necessary information needed for your records.
Basketball Evaluation Form Pdf - Analyze the player’s ability to score from the 2-point range.
Document Specifics
| Fact Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Purpose | The IRS 1040 form is used by individuals to file their annual income tax returns. |
| Filing Status | Taxpayers can select from five filing statuses: Single, Married Filing Jointly, Married Filing Separately, Head of Household, and Qualifying Widow(er). |
| Income Reporting | All sources of income must be reported, including wages, dividends, and interest. |
| Deductions | Taxpayers can choose between the standard deduction and itemized deductions to reduce taxable income. |
| Tax Credits | Various tax credits, such as the Earned Income Tax Credit and Child Tax Credit, can directly reduce the amount of tax owed. |
| Filing Deadline | The standard deadline for filing the 1040 form is April 15th of each year, unless it falls on a weekend or holiday. |
| State-Specific Forms | Many states have their own income tax forms, governed by state laws. For example, California uses Form 540, governed by the California Revenue and Taxation Code. |
How to Write IRS 1040
Filling out the IRS 1040 form is an essential task for individuals who need to report their income and calculate their tax liability. This process requires careful attention to detail to ensure accuracy. Once you complete the form, you will be ready to submit it to the IRS, which may involve additional steps depending on your specific tax situation.
- Gather all necessary documents, including W-2s, 1099s, and any other income statements.
- Begin with the personal information section. Enter your name, address, and Social Security number at the top of the form.
- If applicable, provide information for your spouse and any dependents. This includes their names, Social Security numbers, and relationship to you.
- Report your income. Use the relevant lines to enter wages, salaries, tips, and other sources of income. Be sure to include any taxable interest and dividends.
- Adjust your income as necessary. If you qualify for any adjustments, such as student loan interest or retirement contributions, enter those amounts in the designated areas.
- Calculate your adjusted gross income (AGI) by subtracting your adjustments from your total income.
- Determine your standard deduction or itemized deductions. Choose the method that benefits you the most and enter the appropriate amount.
- Calculate your taxable income by subtracting your deductions from your AGI.
- Refer to the tax tables to find your tax liability based on your taxable income. Enter this amount on the form.
- Account for any tax credits you may qualify for. These can reduce your overall tax bill and should be entered in the designated section.
- Calculate your total tax owed by adding any additional taxes, such as self-employment tax, if applicable.
- Determine if you have already made payments toward your tax liability through withholding or estimated payments. Enter these amounts on the form.
- Calculate whether you owe additional taxes or if you are due a refund.
- Sign and date the form. If filing jointly, your spouse must also sign.
- Make a copy of the completed form for your records before submitting it to the IRS.
Dos and Don'ts
When filling out the IRS 1040 form, it's important to follow certain guidelines to ensure accuracy and compliance. Here are some do's and don'ts to keep in mind:
- Do double-check your personal information, such as your name and Social Security number, for accuracy.
- Do report all sources of income, including wages, dividends, and interest.
- Do take advantage of available deductions and credits that you qualify for.
- Do sign and date your return before submitting it.
- Don't rush through the form; take your time to ensure everything is filled out correctly.
- Don't forget to keep copies of your tax return and any supporting documents for your records.
- Don't ignore IRS correspondence; respond promptly to any inquiries or notices.
Documents used along the form
The IRS 1040 form is the primary document used by individuals to file their annual income tax returns. However, several other forms and documents often accompany it to provide additional information or to report specific types of income and deductions. Here are some of the key forms that may be needed alongside the 1040.
- W-2 Form: This form reports an employee's annual wages and the taxes withheld from their paycheck. Employers must provide this form to employees by the end of January each year.
- 1099 Form: Various versions of this form report income received from sources other than employment, such as freelance work or interest income. Different types of 1099 forms exist, including 1099-MISC and 1099-INT.
- Schedule A: This form is used to itemize deductions, such as medical expenses, mortgage interest, and charitable contributions, instead of taking the standard deduction.
- Schedule C: Self-employed individuals use this form to report income and expenses from their business. It helps determine the net profit or loss for the year.
- Schedule D: This form reports capital gains and losses from the sale of assets like stocks or real estate. Taxpayers must provide details of each transaction for accurate reporting.
- Florida Vehicle POA form 82053: This form is a legal document that allows an individual to authorize another person to act on their behalf in matters related to their vehicle. For more information, visit Florida Forms.
- Form 8862: This form is used to claim the Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC) after it has been disallowed in a previous year. It helps taxpayers demonstrate eligibility for the credit.
In summary, while the IRS 1040 form is essential for filing taxes, these additional forms and documents provide necessary details that can affect tax liability. Gathering all relevant paperwork ensures a smoother filing process and helps taxpayers maximize their deductions and credits.